{{item.title}}
{{item.text}}

{{item.text}}
As we reflect on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, it is apparent that it created the conditions for healthcare systems to deliver better value to patients. Value-based healthcare aims to deliver the best possible outcomes for patients while being efficient in spending. In response to the pandemic, healthcare systems had to organize care differently. While the pandemic has been difficult for healthcare systems, and they have encountered challenges, they have worked hard to safeguard populations. As they reorganized, healthcare systems have made significant strides toward a value-based approach, establishing a patient-centered and data-driven model for delivering healthcare.
Many of the key features of value-based healthcare were validated during the pandemic. At the start, healthcare systems quickly defined centralized goals based on outcomes that mattered most to patients. This definition enabled unprecedented collaboration among stakeholders, including policymakers (such as regulators), providers, payors, and life science companies, to achieve these high-value patient outcomes holistically. Before the pandemic, healthcare systems had struggled to put value-based healthcare into practice. Segmenting the population, defining standardized outcome measures, setting up the technology to collect them, and exchanging leading practices at scale seemed too complex. However, these principles played a vital role in healthcare systems’ response to the pandemic. As the pandemic has progressed, healthcare systems have improved how they manage the disease and have conducted successful vaccination programs. This targeted approach and focus on outcomes has meant the percentage of people being hospitalized and dying from COVID-19 has dramatically decreased, from one in 60 in earlier waves, to fewer than one in 1,000 in the most recent wave.
As a result, the pandemic has swept aside many doubts. No longer can stakeholders claim that delivering value-based healthcare is too abstract or challenging. Instead, the pandemic proved that when stakeholders align toward the common goal of achieving patient outcomes, it creates the conditions for value-based healthcare to start and quickly succeed. Each stakeholder contributed a vital piece of the puzzle to help deliver disruptive solutions that created an integrated value network.
To build on this momentum, healthcare system stakeholders need to exploit the lessons from the COVID-19 response and consider how they can apply those lessons to transform their organizations and healthcare models and achieve higher-value care in a strategic and comprehensive manner.
Value-based healthcare aims to deliver the best possible outcomes for patients while being efficient in spending. This approach reduces the risk of spending time and money on care and treatments that do not contribute to positive outcomes. Value for patients encompasses clinical outcomes and the quality of outcomes. For example, for patients living with diabetes, psychological well-being is just as valuable as maintaining glycemic control.
Healthcare systems must discover which outcomes give patients the most value and then ensure that all stakeholders are focused and incentivized to deliver these outcomes in the most financially efficient manner.
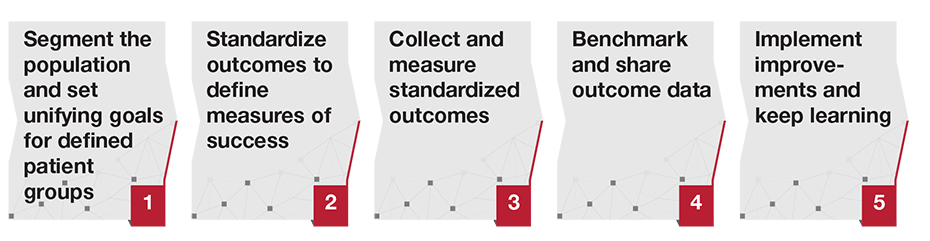
All stakeholders have a role to play in delivering value-based healthcare. Here are five lessons stakeholders can learn from the COVID-19 pandemic to transform other parts of their health system.
1. Segment the population and set unifying goals for defined patient groups
Healthcare systems that have performed well during the pandemic focused on achieving outcomes by segmenting the population and using tailored approaches for identified patient groups. All stakeholders—policymakers, providers, payors, and life science companies—must take a similar approach in order for value-based healthcare to work. These stakeholders must define a target segment of the population, create the appropriate healthcare products and services for this demographic, and deliver them to provide value to the patients and the system.
2. Standardize outcomes to define measures of success
For healthcare system stakeholders to collaborate and deliver outcomes for patients, they need to align their efforts toward achieving a common set of outcomes. Policymakers should ensure that healthcare system stakeholders apply these standards consistently, setting the foundation for stakeholders to collaborate and enabling like-for-like comparison of outcomes later on.
For example, the International Consortium for Health Outcomes Measurement (ICHOM) has published global standards on the outcomes that matter most to patients. This nonprofit organization convenes experts and patients worldwide to define patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) for patients for various conditions, including breast cancer, prostate cancer, diabetes, heart failure, and depression and anxiety.
3. Collect and measure standardized outcomes
Regulators and the public sector should define data standards and establish incentives to collect and report outcomes. They must also ensure that the technological means are available to collect data in a centralized, standardized, and independent manner. In particular, that means using innovative ways to help citizens self-report outcome data and give them access to information on their health status.
Stakeholders can analyze outcome data to identify variations in care and outcomes, enabling them to find the causes of variation, and learn and share leading practices to enhance services.
4. Benchmark and share outcome data
All stakeholders within a value-based healthcare system need to be transparent with their outcome data. By creating a culture of openness, all contributors can share their progress on meeting PROMs and use other stakeholder data to improve their respective services. Regulators and the public sector can play an essential role in establishing outcome registries that support this shared learning and innovation.
Benchmarking outcome data can also help payors inform providers about who their costliest patients are. Such data can help governments focus resources on the socioeconomic determinants of poor health.
As outcome reporting matures, publishing outcomes on a national and global level can help providers and suppliers gain a competitive advantage from the outcomes they are able to achieve. Patients and payors will make more informed decisions based on the outcomes and value they are expected to experience.
5. Implement improvements and keep learning
Value-based healthcare is an ongoing process. Therefore, it is crucial to repeat the cycle of measuring, learning, and improving. Continually, stakeholders need to analyze outcome data, learn from leading practices, implement service improvements, and measure how they contribute to achieving value for patients and the healthcare system.
As part of the learning process, providers should set up forums within their organization to share progress on delivering priority outcomes for patients. By pooling information, providers create accountability and a starting point to reduce variation in care and make care financially efficient. Other specialties and teams can learn from these experiences. They may provide input on how to make services more patient-centered. Providers should join global forums to learn and share leading practices on delivering patient-centered outcomes more effectively.
Payors can use outcome data to work with regulators, introducing value-based payment policies that incentivize providers to deliver high-value patient outcomes and ensure more use of risk-adjusted reimbursement. Life science companies can harness outcome data to assess the efficacy of their products on different patient segments. With these insights, they can develop more effective and personalized treatments, increasing their value to their customers.
As we look ahead, we must utilize and build on the successes health systems have achieved during the COVID-19 pandemic in creating better value for patients. Despite the challenges, healthcare systems worked hard during the pandemic to safeguard populations, and in so doing paved the way for value-based healthcare. In the future, focus and collaboration among all healthcare stakeholders will be critical to transforming care for other conditions and diseases. When stakeholders align on delivering the same high-value outcomes, potent and disruptive change will follow, generating exceptional outcomes for patients and the wider population.



Menu